Posted On: October 16, 2024
Oral cancer is a serious health issue that can develop in the mouth, lips, and throat. While various factors contribute to its onset, one critical link that many are unaware of is the connection between human papillomavirus (HPV) and oral cancer. With October being dedicated to cancer awareness, now is the perfect time to educate yourself on the risks and preventive measures associated with HPV-related oral cancer.
Oral cancer refers to any cancerous growth located in the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, and throat. It is one of the most common forms of cancer globally, with thousands of new cases diagnosed each year. While early-stage oral cancer can often be treated successfully, late-stage diagnoses can be life-threatening.
Recognizing the early signs of oral cancer can significantly increase survival rates. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of more than 150 related viruses, some of which are sexually transmitted. HPV is highly common, and most people will contract it at some point in their lives. In many cases, the infection clears up on its own without causing significant health issues. However, certain high-risk strains of HPV can lead to various types of cancer, including cervical, anal, and oral cancers.
HPV infections can affect the mouth and throat through oral contact, including kissing and oral sex. When a high-risk strain of HPV infects the cells in the mouth, it can lead to changes in those cells, increasing the risk of developing oral lesions. Over time, these lesions may become cancerous if left untreated.
There are several strains of HPV, but the ones most strongly linked to oral cancer are HPV-16 and HPV-18. HPV-16, in particular, has been found to play a significant role in oropharyngeal cancers (cancers of the throat, tonsils, and base of the tongue). Research indicates that individuals infected with HPV-16 are at a much higher risk of developing oral cancer compared to those without the virus.
Tobacco and alcohol use remain two of the most significant risk factors for developing oral cancer, especially when combined with an HPV infection. Smoking damages the cells lining the mouth and throat, making it easier for HPV to take hold and cause long-term damage. Similarly, heavy alcohol use weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
A weakened immune system can make it more difficult for your body to clear an HPV infection. People with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV or those undergoing treatments like chemotherapy, are at a higher risk of HPV-related oral cancer.
HPV-related oral cancer affects more men than women, though the reasons for this are not fully understood. Additionally, individuals between the ages of 40 and 60 are most at risk for developing this form of cancer. However, cases in younger adults have been increasing, largely due to changing patterns of sexual behavior and increased HPV transmission.
Routine dental check-ups are crucial for the early detection of oral cancer. Dentists can identify suspicious changes in the mouth, such as precancerous lesions, before they become serious. Regular screenings are especially important for individuals at higher risk due to HPV infection, smoking, or excessive alcohol use.
One of the most effective ways to prevent HPV-related cancers is through vaccination. The HPV vaccine, commonly given during adolescence, can protect against the high-risk strains of HPV that cause most cases of cervical and oral cancer. The vaccine is most effective when administered before individuals become sexually active, though it can still offer protection to adults.
Lifestyle adjustments can also play a critical role in reducing the risk of developing oral cancer. These changes may include:
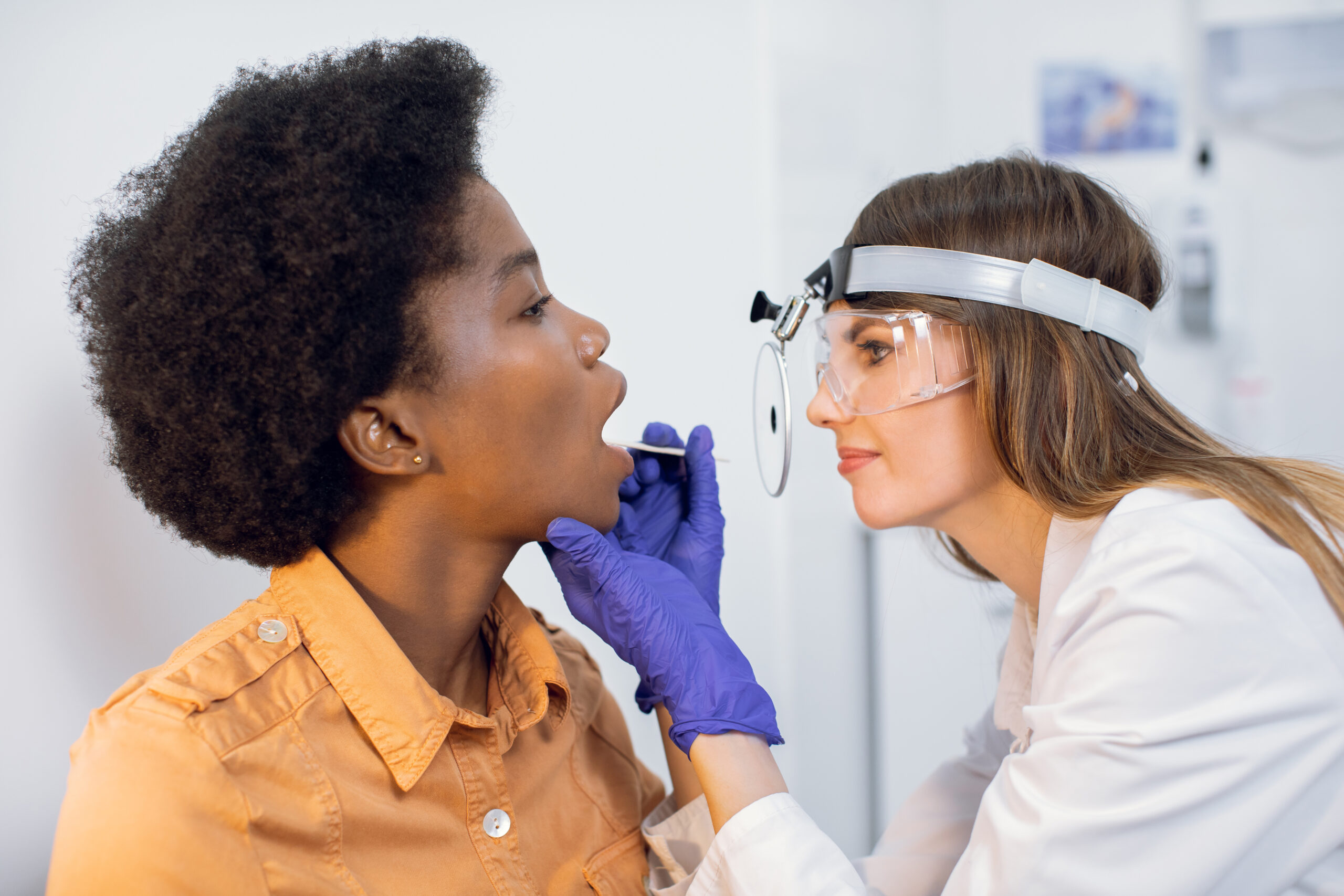
Dentists are often the first healthcare professionals to spot early signs of oral cancer. During a routine exam, your dentist will check for abnormalities in the mouth, including suspicious sores or lumps that could indicate cancer. These screenings can catch cancer at an early stage, improving the chances of successful treatment.
At Pennington Family Dentistry, we understand the importance of early detection. Our team offers thorough oral cancer screenings as part of every routine dental visit. Using the latest technology and techniques, we examine the mouth, lips, and throat for any signs of abnormal tissue, ensuring that you receive prompt treatment if necessary.
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for oral cancer. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, your doctor may remove the cancerous tissue along with some surrounding healthy tissue to prevent the spread of the disease. In more advanced cases, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to restore the function and appearance of the affected area.
In addition to surgery, patients may undergo radiation therapy or chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target cancer cells, while chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy them. These treatments may be used alone or in combination, depending on the stage of the cancer.
While cancer treatments can be highly effective, they often come with side effects such as dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, and changes in taste. At Pennington Family Dentistry, we work closely with patients undergoing cancer treatment to help manage these side effects and maintain their oral health during recovery.
Oral cancer can develop silently and without warning, but early detection could save your life. At Pennington Family Dentistry, we are committed to providing comprehensive oral cancer screenings to help keep you healthy. Schedule your appointment today and take the first step in protecting your oral health.